Video Ingestion
MemoryGrid supports video ingestion through GStreamer, an external system built on top of MemoryGrid.
Architecture
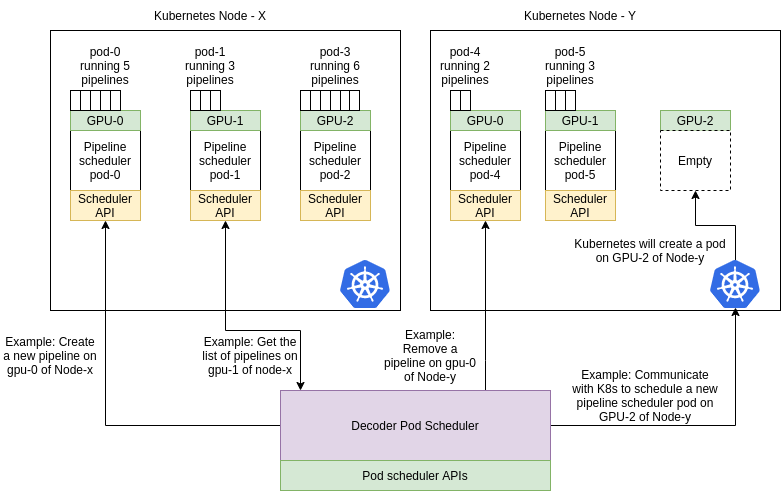
The Decoder Scheduler creates and manages video decoding pipelines on Kubernetes. The video decoding architecture is organized into two primary components:
1. Decoder Pod Scheduler
The Decoder Pod Scheduler is responsible for deploying and managing decoder pods across Kubernetes cluster nodes. It interacts directly with the Kubernetes API and provides the following REST APIs:
- Create a decoder pod
- Destroy a decoder pod
- List all active decoder pods
Each decoder pod created by this service runs a Decoding Pipeline Scheduler, which exposes its own web server for managing individual video pipelines.
2. Decoding Pipeline Scheduler
Each pod managed by the Decoder Pod Scheduler acts as a Pipeline Scheduler, capable of managing multiple decoding pipelines based on the node’s available CPU and GPU resources. The responsibilities of the Pipeline Scheduler include:
- Running a web service to handle pipeline creation and removal requests.
- Launching each pipeline as a separate process inside the pod.
- Maintaining an internal mapping of process IDs (PIDs) to source IDs.
- Terminating pipelines by killing the corresponding PID upon receiving a removal request.
Overall Flow
The diagram above illustrates the full architecture of the video decoding system in AIOS:
- The Decoder Pod Scheduler deploys Pipeline Scheduler pods to the appropriate GPU-enabled nodes.
- Each Pipeline Scheduler pod manages the lifecycle of multiple pipelines, running them as independent processes.
- These pods expose APIs to create, list, and remove individual pipelines.
- All Pipeline Scheduler pods are orchestrated and managed by the Decoder Pod Scheduler, which handles communication with the Kubernetes cluster.
API Usage
The decoder system exposes a set of APIs, but direct usage by end users is not recommended, as these APIs require numerous configuration parameters. Instead, the AIOS Master DAG Controller handles:
- Dynamic creation and management of decoder pipelines
- Configuration updates based on workload and video stream metadata
However, read-only APIs (such as listing pipelines) may be used externally for monitoring and querying purposes.
Creating GStreamer Ingestion Pods
MemoryGrid supports dynamic creation and removal of GStreamer ingestion pods via a Decoder Pod Scheduler. These pods run decoding pipelines on GPU-enabled Kubernetes nodes. The APIs interact with the Kubernetes cluster to create or remove decoding pods and their associated services.
1. POST /createInstance
Creates a new decoder pod and its associated Kubernetes service on the specified node and GPU.
Description
This API provisions a GStreamer ingestion pod on a target node and GPU by creating a Kubernetes Deployment and a corresponding Service. The pod runs a decoding pipeline scheduler which can later be queried or controlled via other APIs.
Request Payload
{
"node": "<NODE_NAME>",
"gpuID": "<GPU_ID>"
}
node(string): The name of the Kubernetes node on which the pod should be scheduled.gpuID(string or int): The GPU ID on the node where the decoder pod should be attached.
Response
{
"success": true,
"payload": {
"service_create_result": "Created service successfully",
"pod_create_result": "Created pod successfully"
}
}
If an error occurs:
{
"success": false,
"payload": "Error message"
}
cURL Example
curl -X POST http://<HOST>:5000/createInstance \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"node": "node-1",
"gpuID": "0"
}'
2. POST /removeInstance
Removes an existing decoder pod and its Kubernetes service from the specified node and GPU.
Description
This API deletes the Kubernetes Deployment and Service associated with the decoder pod running on the specified node and GPU. It performs a graceful termination of the pod using foreground deletion.
Request Payload
{
"node": "<NODE_NAME>",
"gpuID": "<GPU_ID>"
}
node(string): The name of the Kubernetes node where the decoder pod is deployed.gpuID(string or int): The GPU ID associated with the pod to be deleted.
Response
{
"success": true,
"payload": {
"service_remove_result": "Removed service successfully",
"pod_remove_result": "Remove pod successfully"
}
}
If an error occurs:
{
"success": false,
"payload": "Error message"
}
cURL Example
curl -X POST http://<HOST>:5000/removeInstance \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"node": "node-1",
"gpuID": "0"
}'
Creating Video Ingestion pipelines
These APIs delegate control operations (query, start, restart) to individual Pipeline Scheduler pods, which are exposed via Kubernetes Services. These services are dynamically constructed using the format:
http://decoder-<node>-gpu-<gpuID>-svc.framedb-storage.svc.cluster.local:5000
3. POST /queryHealth
Fetches the health status of the decoder pod on the specified node and GPU.
Request Payload
{
"node": "<NODE_NAME>",
"gpuID": "<GPU_ID>"
}
Response
{
"success": true,
"payload": {
"status": "healthy",
"uptime": "17300s",
"version": "v1.2.3"
}
}
cURL Example
curl -X POST http://<HOST>:5000/queryHealth \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"node": "node-1", "gpuID": "0"}'
4. POST /querySources
Returns a list of all active decoding streams (pipelines) running on the specified decoder pod.
Request Payload
{
"node": "<NODE_NAME>",
"gpuID": "<GPU_ID>"
}
Response
{
"success": true,
"payload": [
{
"jobName": "camera01-decoder",
"config": {
"uri": "rtsp://example.com/stream1",
"codec": "h264"
}
},
{
"jobName": "camera02-decoder",
"config": {
"uri": "rtsp://example.com/stream2",
"codec": "h265"
}
}
]
}
cURL Example
curl -X POST http://<HOST>:5000/querySources \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"node": "node-1", "gpuID": "0"}'
5. POST /restartSource
Restarts a specific stream by first killing and then recreating the decoding job using the previously stored configuration.
Request Payload
{
"node": "<NODE_NAME>",
"gpuID": "<GPU_ID>",
"sourceId": "<SOURCE_ID>"
}
- The job name is derived internally as:
<SOURCE_ID>-decoder.
Response
{
"success": true,
"payload": "Stream source-1 restarted successfully"
}
cURL Example
curl -X POST http://<HOST>:5000/restartSource \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"node": "node-1",
"gpuID": "0",
"sourceId": "camera01"
}'
6. POST /startWithContext
Starts a new decoding pipeline with full configuration context.
Request Payload
{
"node": "<NODE_NAME>",
"gpuID": "<GPU_ID>",
"sourceId": "<SOURCE_ID>",
"config": {
}
}
- Internally constructs a job name:
<SOURCE_ID>-decoder - Wraps the config under
jobParameters.settings.sourceInfo
Response
{
"success": true,
"payload": "Stream started with context"
}
cURL Example
curl -X POST http://<HOST>:5000/startWithContext \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"node": "node-1",
"gpuID": "0",
"sourceId": "camera01",
"config": {}
}'
7. POST /restartWithContext
Performs a complete restart of a decoding pipeline using the supplied configuration.
Request Payload
Same structure as /startWithContext.
Behavior
- Constructs the job name (
<sourceId>-decoder) - Sends a
POST /killStreamrequest to terminate the job - Waits for 5 seconds
- Sends a
POST /createStreamrequest with the context payload
Response
{
"success": true,
"payload": "Stream restarted with context"
}
cURL Example
curl -X POST http://<HOST>:5000/restartWithContext \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"node": "node-1",
"gpuID": "0",
"sourceId": "camera01",
"config": {}
}'
Source Registry
The Source Registry is a central metadata store for video sources. It manages metadata for live (ONVIF, RTSP, etc.) and offline (archived) video feeds. Each source is associated with a unique sourceID and can be grouped under a groupID.
Sources may include parameters like:
- Video encoding format
- Frame resolution and FPS
- Stream or storage paths
- Optional ONVIF credentials and calibration metadata
- Optional geospatial location via
geoJson
This registry is useful for video ingestion pipelines, computer vision workflows, or distributed video analytics systems.
Schema
Here is the revised schema explanation table using "Yes" or "No" for the Required column, with no emojis:
Source Registry Schema Explanation
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
sourceID |
String | Yes | Unique identifier for the video source. |
groupID |
String | Yes | Identifier used to group related sources. |
label |
String | Yes | Human-readable name or label for the source. |
description |
String | No | Optional textual description of the source. |
sourceType |
String | Yes | Type of source: for example, live or offline. |
liveSourceInfo |
Object | No | Metadata and connection details for live sources. |
offlineVideo |
Object | No | Metadata and storage details for offline video files. |
sourceMetadata |
Object | No | Metadata such as frame properties and calibration data. |
└─ frameProperties |
Object | Yes | Video frame dimensions and encoding format. |
└─ width |
Number | Yes | Width of the video frame in pixels. |
└─ height |
Number | Yes | Height of the video frame in pixels. |
└─ encodingFormat |
String | No | Optional encoding format (e.g., H.264). |
└─ calibrationData |
Mixed | No | Optional calibration parameters (camera configuration, etc.). |
alerts |
Mixed | No | Optional alerting or event metadata associated with the source. |
liveSourceInfo Subschema
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
protocol |
String | Yes | Streaming protocol (e.g., RTSP, ONVIF). |
streamURL |
String | Yes | URL of the video stream. |
onvifURL |
String | Yes | URL for ONVIF device interface. |
onvifAuthInfo |
Mixed | No | Optional ONVIF authentication credentials. |
isOnvifAuth |
Boolean | Yes | Indicates whether ONVIF auth is required. |
streamParameters |
Object | Yes | Details about the stream format. |
└─ codec |
String | Yes | Codec used for video encoding (e.g., H.264). |
└─ fps |
Number | Yes | Frames per second of the live stream. |
└─ bitrate |
Number | No | Optional bitrate of the stream. |
geoJson |
Mixed | No | Optional geolocation data in GeoJSON format. |
offlineVideo Subschema
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
container |
String | Yes | Video file container format (e.g., mp4, mkv). |
storageVideoPath |
String | Yes | Path or URI to the stored video file. |
videoParameters |
Object | Yes | Video encoding and playback properties. |
└─ codec |
String | Yes | Codec used for the stored video. |
└─ fps |
Number | Yes | Frames per second. |
└─ bitrate |
Number | No | Optional video bitrate. |
geoJson |
Mixed | No | Optional geolocation data in GeoJSON format. |
Base URL
POST http://<host>:<port>/api/source
Content-Type: application/json
API Endpoints
1. Check if Source Exists
POST /sourceExists
Checks if a source with a given sourceID exists in the registry.
Request:
{
"sourceID": "camera-001"
}
cURL:
curl -X POST http://localhost:3000/api/source/sourceExists \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"sourceID": "camera-001"}'
Response:
{
"error": false,
"payload": { ...source document... }
}
2. Create New Source
POST /createNew
Creates a new source if it doesn't already exist.
Request:
{
"sourceID": "camera-001",
"groupID": "group-A",
"label": "Main Gate Cam",
"sourceType": "LIVE",
"liveSourceInfo": {
"protocol": "RTSP",
"streamURL": "rtsp://example.com/live",
"onvifURL": "http://example.com/onvif",
"isOnvifAuth": false
}
}
cURL:
curl -X POST http://localhost:3000/api/source/createNew \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d @new-source.json
Response:
{
"error": false,
"payload": { ...created source... }
}
3. ✏️ Update Existing Source
POST /updateSource
Updates the fields of an existing source using sourceID.
Request:
{
"sourceID": "camera-001",
"data": {
"label": "Updated Label",
"description": "Camera updated"
}
}
cURL:
curl -X POST http://localhost:3000/api/source/updateSource \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d @update-source.json
Response:
{
"error": false,
"payload": {
"acknowledged": true,
"modifiedCount": 1,
"matchedCount": 1
}
}
4. Get Source by SourceID
POST /getBySourceID
Returns the source document(s) with the specified sourceID.
Request:
{
"sourceID": "camera-001"
}
cURL:
curl -X POST http://localhost:3000/api/source/getBySourceID \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"sourceID": "camera-001"}'
5. Get All Sources by Group
POST /getSourcesByGroup
Fetches all sources belonging to a given groupID.
Request:
{
"groupID": "group-A"
}
cURL:
curl -X POST http://localhost:3000/api/source/getSourcesByGroup \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"groupID": "group-A"}'
6. Query Sources
POST /query
Perform arbitrary MongoDB-style queries on the source registry.
Request:
{
"query": {
"sourceType": "LIVE",
"groupID": "group-A"
}
}
cURL:
curl -X POST http://localhost:3000/api/source/query \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d @query.json
Remove by SourceID
POST /removeBySourceID
Deletes all documents with the given sourceID.
Request:
{
"sourceID": "camera-001"
}
cURL:
curl -X POST http://localhost:3000/api/source/removeBySourceID \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"sourceID": "camera-001"}'
8. Remove by GroupID
POST /removeByGroupID
Deletes all sources that belong to the specified groupID.
Request:
{
"groupID": "group-A"
}
cURL:
curl -X POST http://localhost:3000/api/source/removeByGroupID \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"groupID": "group-A"}'
GStreamer ingestion pod
Overview
MemoryGrid's video decoding infrastructure uses GStreamer (GST) to dynamically construct and run multimedia pipelines for live streams and stored videos. Decoder pods are deployed on GPU-enabled Kubernetes nodes. Each pod launches decoding pipelines as independent processes and is orchestrated by a central Decoder Scheduler.
This document provides a complete overview of:
- What a GStreamer pipeline is
- The role and behavior of the
run_task()function - Accepted configuration parameters and their effect on pipeline construction
- How decoder pipelines are assembled for different video sources
1. What is a GStreamer Pipeline?
A GStreamer pipeline is a string-based description of connected multimedia components, called elements, that process media data in stages. For example:
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=video.mp4 ! decodebin ! autovideosink
In this command:
filesrcreads a media filedecodebinautomatically detects the format and decodes itautovideosinkdisplays the video
MemoryGrid dynamically assembles such pipelines based on source metadata and user configurations, optimizing for GPU or CPU-based decoding.
2. run_task() Entry Function
The run_task() function is the execution entrypoint inside each decoder pod. It performs the following high-level steps:
- Reads and parses the input config from
env_settings.source_data - Validates required fields and their types
-
Based on the
modeparameter, launches either: -
LiveDecoder– for RTSP/live sources StoredVideoDecoder– for file-based stored video
3. Configuration Parameters
The run_task() function accepts a JSON payload via the environment variable env_settings.source_data. This payload is a dictionary of parameters used for pipeline construction, routing, metadata fetching, and runtime behavior.
Below is a table listing the supported configuration parameters.
Decoder Input Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
source_id |
String | Yes | Unique identifier for the stream/video source. |
mode |
String | Yes | Specifies decoding mode. Allowed: "live" or "video". |
url |
String | Yes | RTSP URL or file path to the input video source. |
routing_url |
String | Yes | Base URL of the MemoryGrid API to query node mappings. |
routing_api |
String | Yes | API path appended to routing_url to perform routing query. |
use_gpu |
Boolean | Yes | Use GPU-accelerated decoding (nvh264dec, nvjpegdec) or fallback to CPU. |
container |
String | No | Required only for stored videos. Allowed: "mp4", "mkv", "flv". |
loop_video |
Boolean | Yes | Whether to loop the video endlessly. |
duration |
Integer | Yes | Total duration in seconds to run the decoding job. |
color_format |
String | Yes | Output video color format. Example: "RGB", "BGR". |
update_counter |
Integer | Yes | Frequency of update messages to MemoryGrid. |
frame_quality |
Integer | Yes | JPEG/PNG quality for output frames (0–100). |
retry_interval |
Integer | Yes | Retry wait time in seconds after decoding failure. |
updates_url |
String | Yes | Redis or MemoryGrid update channel URL. |
updates_port |
Integer | Yes | Port used to send update messages. |
updates_password |
String | Yes | Password to authenticate update channel access. |
is_sentinel |
Boolean | Yes | Whether Redis uses sentinel-based configuration. |
act_svc |
String | Yes | Hostname of the actuation controller. |
act_port |
Integer | Yes | Port of the actuation controller. |
act_password |
String | Yes | Password for actuation controller access. |
fps_checker_max_interval |
Integer | No | Maximum time in seconds for FPS validation. Default: 30. |
fps_checker_min_frames |
Integer | No | Minimum frame count to validate FPS. Default: 5. |
enable_fps_checker |
Boolean | No | Whether to enable internal framerate validation. |
use_custom_ts |
Boolean | No | Manually add timestamps to stored video output. |
as_live |
Boolean | No | Treat stored video as live for encoder compatibility. |
4. Decoder Pipeline Construction
Based on the input parameters, the decoding pipeline is assembled in three major stages:
A. Decoder Unit
This part fetches the source and decodes it into raw frames.
| Source Mode | Pipeline Snippet Example |
|---|---|
live (RTSP) |
rtspsrc location="<url>" ! rtph264depay ! h264parse ! nvh264dec |
video (Stored) |
filesrc location="<file>" ! qtdemux ! h264parse ! nvh264dec |
B. Branch Unit
This section prepares the decoded video for resizing, color conversion, and batching.
| Mode | Snippet |
|---|---|
| GPU | cudaupload ! cudaconvert ! video/x-raw(memory:CUDAMemory), format=<color> ! cudadownload |
| CPU | videoconvert ! video/x-raw, format=<color> |
C. Encoder Unit
Final stage that either batches, streams, or writes the output to MemoryGrid.
| Mode | Snippet |
|---|---|
| Stored video | video_writer |
| Live - batched | video_batcher name=mixer |
| Raw sink | tidbsink name=mixer |
5. Environment Export to GStreamer (FRAMEDB_C)
A JSON blob named FRAMEDB_C is constructed and injected into the environment of the decoding process. This environment contains:
- Target resolutions
- Skip frame thresholds
- Actuation metadata
- Redis update configuration
- Color formatting and quality
- MemoryGrid routing references
This environment is used by internal MemoryGrid GStreamer plugins to perform intelligent encoding, storage, and routing decisions.
6. Example Input Configuration
Here is an example source_data input for a stored video pipeline:
{
"source_id": "camera01",
"mode": "video",
"url": "/mnt/videos/sample.mp4",
"container": "mp4",
"routing_url": "http://framedb-router:5000",
"routing_api": "/getMapping",
"use_gpu": true,
"loop_video": true,
"duration": 600,
"color_format": "RGB",
"update_counter": 10,
"frame_quality": 90,
"retry_interval": 60,
"updates_url": "redis://updates.framedb",
"updates_port": 6379,
"updates_password": "abc123",
"is_sentinel": false,
"act_svc": "actuation.framedb",
"act_port": 9000,
"act_password": "xyz123"
}
GStreamer pipeline structure
MemoryGrid dynamically constructs GStreamer pipelines based on source type (stored or live), codec, hardware capabilities (GPU/CPU), and downstream requirements. The final pipeline is composed of three logical sections:
- Decoder Unit – Fetches and decodes video input
- Branch Unit – Processes decoded frames (resizing, color format, scaling)
- Encoder Unit – Sends frames to the MemoryGrid sink
A. Final Pipeline: Stored Video
Example (GPU-enabled, H264, MP4):
filesrc location="/videos/sample.mp4" ! qtdemux ! h264parse ! nvh264dec ! fps_checker ! videorate ! "video/x-raw, framerate=(fraction)8/1" ! cudaupload ! cudaconvert ! "video/x-raw(memory:CUDAMemory), format=RGB" ! cudadownload ! video_writer
Plugin-by-Plugin Explanation:
| Plugin | Description |
|---|---|
filesrc location=... |
Reads the video file from local filesystem. |
qtdemux |
Demultiplexes MP4 container into audio/video streams. |
h264parse |
Parses raw H.264 byte stream to extract frames and metadata. |
nvh264dec |
NVIDIA GPU-based decoder for H.264 streams. |
fps_checker (optional) |
Custom plugin that validates if incoming FPS is within expected bounds. |
videorate |
Regulates frame rate by dropping/duplicating frames as needed. |
video/x-raw, framerate=(fraction)8/1 |
Caps filter enforcing target output frame rate (e.g., 8 FPS). |
cudaupload |
Uploads CPU video frames to GPU memory. |
cudaconvert |
Converts format/colorspace within GPU (e.g., NV12 → RGB). |
video/x-raw(memory:CUDAMemory), format=RGB |
Applies GPU memory layout and output format. |
cudadownload |
Downloads processed video frames from GPU to CPU. |
video_writer |
Custom plugin that encodes/writes output to MemoryGrid in stored mode. |
B. Final Pipeline: Live Video Stream
Example (GPU-enabled, MJPEG via RTSP):
rtspsrc protocol=tcp location="rtsp://camera" latency=10 ! rtpjpegdepay ! jpegparse ! nvjpegdec ! fps_checker ! videorate ! "video/x-raw, framerate=(fraction)8/1" ! cudaupload ! cudaconvert ! "video/x-raw(memory:CUDAMemory), format=BGR" ! cudadownload ! tee name=t t. ! queue ! mixer.
Plugin-by-Plugin Explanation:
| Plugin | Description |
|---|---|
rtspsrc protocol=tcp location=... |
Fetches video from a remote RTSP stream using TCP. |
latency=10 |
Buffers 10ms worth of data to smooth out jitter. |
rtpjpegdepay |
Extracts JPEG payloads from RTP packets. |
jpegparse |
Parses JPEG stream and prepares it for decoding. |
nvjpegdec |
NVIDIA GPU decoder for MJPEG-encoded frames. |
fps_checker (optional) |
Checks actual frame delivery against target FPS. |
videorate |
Controls output frame rate to match required target. |
video/x-raw, framerate=(fraction)8/1 |
Frame rate control (e.g., 8 FPS). |
cudaupload |
Transfers CPU frames to GPU memory. |
cudaconvert |
Color format conversion in GPU. |
video/x-raw(memory:CUDAMemory), format=BGR |
Specifies output format and memory layout. |
cudadownload |
Transfers processed frames back to CPU. |
tee name=t |
Splits pipeline to multiple branches (for multi-resolution or multi-process ingestion). |
queue |
Buffers frames between split branches to prevent pipeline stalls. |
mixer. |
Sends video to FrameDB’s live ingestion system (e.g., for batching or actuation). |
Optional Elements That May Be Present
| Plugin | Used When | Description |
|---|---|---|
timestamper |
use_custom_ts=true |
Applies custom timestamp metadata (typically for stored video). |
videoscale, cudascale |
If scaling is required | Resize the frame to target dimensions (per MemoryGrid node specs). |
videoconvert |
In CPU pipelines | Converts between colorspaces or pixel formats in CPU. |
jpegdec, avdec_h264, avdec_h265 |
When use_gpu=false |
Software decoders used when GPU decoding is disabled. |